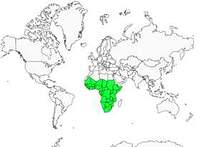
Black Crake
Zapornia flavirostra - Râle à bec jaune Marouette à bec jaune
Identification
Adults, males and females as there is no sexual dimorphism, are black. With good lighting and a good approach, the back, chest, and sides are slate black, the wings are olive-brown. The tail is black, and the beak is bright yellow. Paws, toes, and eyes red, with a red orbital ring make identification easy. In eclipse plumage, paws and toes are duller.
The immature is lighter, steel-blue replacing the adult's black. The beak is very dark yellow-green, paws and toes are dull red to brown, and the eyes are red. The downy chick is black with a pale pink beak.
Subspecific information monotypic species
Foreign names
- Râle à bec jaune,
- Polluela negra africana,
- franga-de-água-preta,
- Schwarzkielralle,
- mór vízicsibe,
- Zwart Porseleinhoen,
- Rallo nero,
- korpsumphöna,
- Svartrikse,
- chriašť mníšsky,
- chřástal žlutozobý,
- Sort Rørvagtel,
- mustahuitti,
- Swartriethaan,
- polla negra,
- Sótrella,
- kureczka czarna,
- melnais ormanītis,
- vranja tukalica,
- Африканский чёрный пастушок,
- アフリカクロクイナ,
- 黑苦恶鸟,
- korpsumphöna,
- 黑苦惡鳥,
Voice song and call
The species, discreet during the year, becomes expressive and noisy during the breeding season. The song of the Black Crake is strong and deep and is performed in duet. One individual well hidden in the vegetation emits a guttural sound krrrok-kraaaa, the other responds crroo-crrr-crrr-coo in a softer way. Other individuals can join in on these conversations and increasingly louder and noisier exchanges can then be heard over the water vegetation. Chip is a warning cry, pruk is a contact call.
Habitat
The Black Crake is a water bird. It can be found from sea level up to 3,000 metres. It frequents a large variety of wetland habitats as long as they have good levels of flooding, substantial and permanent vegetation cover where it can hide and nest.
Behaviour character trait
The Black Crake is a discreet bird that is heard more often than it is seen. Sedentary, it has local migratory movements that are more related to precipitation than to large seasonal migrations.
It can be observed as an individual or in pairs. It is active throughout the day with peaks of activity after heavy rains. It feeds in wet areas, on floating vegetation where it can easily walk with its long toes or climb the higher covers like reeds or shrubs. Dry areas are also feeding sites. The luckiest observers can see it in the open and even on the backs of hippos and warthogs where it looks for skin parasites. The Black Crake is monogamous and can reproduce all year round as long as the conditions are suitable, but much more according to the rainy season. During this period it is territorial and extremely aggressive towards other birds, especially with other rallidae. It is observed in pairs and sometimes in groups of up to 10 individuals. Common nuptial parades of the family are made in the form of food offerings and feather smoothing. Pursuits between the two partners before mating are also frequent. Between December and March adults remain under the vegetation cover for up to 3 weeks during moulting.Dietfeeding habits
Black Crake feeds on aquatic invertebrates, fish, crabs, shrimp, frogs and other animals. It also eats flying insects, butterflies, bees, wasps, grasshoppers and flying ants which it snatches in mid-air, on the backs of hippopotamuses and when it climbs into vegetation. Its diet also includes bird eggs, as well as chicks such asthose of weavers or herons. This is supplemented by seeds and other parts of aquatic plants, lentils and lilies. Sometimes it may feed on carrion found near the water.
Reproduction nesting
The Black Crake builds its nest at a height, between 20 and 50 cm above the water, sometimes as high as 3 metres in a bush and in cover to avoid predators whilst still being close to its source of food.
The nest can also be made on the ground in a tuft of grass or on vegetation. It is cup-shaped and is constructed by the two sexes, out of reeds, Carex and other aquatic plants. The female lays between 2 and 6 eggs, usually 3, white-cream spotted with brown. The two parents incubate them for 13-19 days and are sometimes aided by older members of the previous year's generation. The nestlings leave the nest no more than 3 days after hatching but are still fed and protected by the parents for several weeks. They become flight-ready at 5-6 weeks, independent between 6 and 12 weeks and remain in the family group until the next breeding season. The species can produce up to 4 broods in the season.Threats - protection
IUCN conservation status
concern
in the Wild
threatened
evaluated
The Black Crake is common in its distribution area. It has adapted easily to artificial or temporary wet areas that it can easily find if needed. Its unpleasant flesh to eat allows it not to be hunted. The trend of the population is difficult to establish due to uncertainties about the impacts of habitat modification on the size of the population.
Sources of information
- IOC World Bird List (v14.2), Gill, F and D Donsker (Eds). 2024-04-18.
- Birds of Kenya and Northern Tanzania, Dale A Zimmerman, Donald A Turner, David J Pearson
- Birds of Southern Africa, Tony Roocroft
- BirdLife International, BirdLife International
Other sources of interest
 Specification sheet created on
24/07/2023 by Nathalie Santa Maria
Specification sheet created on
24/07/2023 by Nathalie Santa MariaTranslation by AI Oiseaux.net
© 1996-2025 Oiseaux.net
- Accipitriformes
- Aegotheliformes
- Anseriformes
- Apodiformes
- Apterygiformes
- Bucerotiformes
- Caprimulgiformes
- Cariamiformes
- Casuariiformes
- Charadriiformes
- Ciconiiformes
- Coliiformes
- Columbiformes
- Coraciiformes
- Cuculiformes
- Eurypygiformes
- Falconiformes
- Galliformes
- Gaviiformes
- Gruiformes
- Leptosomiformes
- Mesitornithiformes
- Musophagiformes
- Nyctibiiformes
- Opisthocomiformes
- Otidiformes
- Passeriformes
- Pelecaniformes
- Phaethontiformes
- Phoenicopteriformes
- Piciformes
- Podargiformes
- Podicipediformes
- Procellariiformes
- Psittaciformes
- Pterocliformes
- Rheiformes
- Sphenisciformes
- Steatornithiformes
- Strigiformes
- Struthioniformes
- Suliformes
- Tinamiformes
- Trogoniformes