Lanner Falcon
Falco biarmicus - Faucon lanier
Identification
Falcons (from latin falco, falconis, who has nails in the shape of a scythe) are small birds of prey. Beak is short and bended from the base.
Lanner falcons have a similar size to the Peregrine Falcon, but have a paler coloration.
Their tail is longer and their wings are less pointed. Their appearance is svelter and they fly with a less powerful wings beat. Head cap looks like a reddish hood and forehead is white. A slim black moustache appears across the cheeks, just under the dark iris. Orbital circle is pale. Beak is greyish blue. Back is uniformly slate grey, showing little contrast with their rather pale belly. This one has a dominant creamy white or reddish color.
Lanner Falcons are divided into Feldeggi breed in Europe and Erlangeri breed, in North Africa. The latter is a bit smaller, with less spotted and paler underparts, and a darker grey back.
Juveniles of both breeds are much slimmer, with a brownish back and dark streaked underparts.
Subspecific information 5 subspecies
- Falco biarmicus biarmicus (DRCongo to s Kenya south to South Africa)
- Falco biarmicus feldeggii (Italy to Turkey, Azerbaijan and nw Iran)
- Falco biarmicus erlangeri (nw Africa)
- Falco biarmicus tanypterus (ne Africa to Arabia, Israel and Iraq)
- Falco biarmicus abyssinicus (s Mauritania to Ethiopia and Somalia south to Cameroon and n Kenya)
Foreign names
- Faucon lanier,
- Halcón borní,
- alfaneque,
- Lannerfalke,
- Feldegg-sólyom,
- Lannervalk,
- Lanario,
- slagfalk,
- Slagfalk,
- sokol laner,
- raroh jižní,
- Lannerfalk,
- keltapäähaukka,
- Edelvalk,
- falcó llaner,
- Slagfálki,
- raróg górski,
- rudgalvas piekūns,
- južni sokol,
- Ланнер,
- ラナーハヤブサ,
- 地中海隼,
- slagfalk,
- 地中海隼,
Habitat
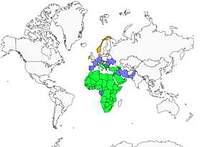
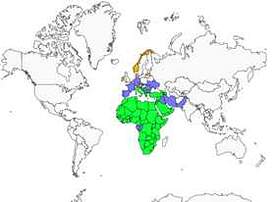
Lanner falcons live on African seashores as well as in continental areas, from Mauritania to Egypt. It can be found also in Italy, Balkanic peninsula, Turkey and Asia Minor in its whole.
In Africa, it nests in semi desertic areas of Moroccan Atlas up to Lybia and dry savannahs. In Europe, it lives in rocky areas with steep cliffs, and also on littoral cliffs.
Behaviour character trait
Lanner falcons live in pair but practice group hunting. Female acts like a beater and hunts out victims while the male remains a bit behind, ready to swoop down on the prey. This technique, rather unusual amongst birds of prey, offers this sedentary bird enough food resources for its survival.
Dietfeeding habits
Reproduction nesting
Normally, Lanner Falcons don't build their nest. They prefer to reuse corvidae's old nests or diurnal birds of prey abandoned eyries, placed on a ledge, a sheer promontory or a tree. Female lays two to five eggs between mid-February and end of March. Both parents sit on alternatively for about 30-35 days. Youngs fledge at about 40 days after hatching.
Threats - protection
IUCN conservation status
concern
in the Wild
threatened
evaluated
Considered as endangered species in the EEC, where its population doesn't exceed 200 pairs. Unfortunately it happens that eggs are stolen by collectors. This poaching has been very harmful to the conservation of the species in Europe. Another cause of low productivity is disturbance caused to this species during breeding season.
Sources of information
- IOC World Bird List (v14.2), Gill, F and D Donsker (Eds). 2024-04-18.
Other sources of interest
 Specification sheet created on
27/07/2006 by Didier Collin with help of Daniel Le-Dantec
Specification sheet created on
27/07/2006 by Didier Collin with help of Daniel Le-DantecTranslation text by
© 1996-2025 Oiseaux.net
- Accipitriformes
- Aegotheliformes
- Anseriformes
- Apodiformes
- Apterygiformes
- Bucerotiformes
- Caprimulgiformes
- Cariamiformes
- Casuariiformes
- Charadriiformes
- Ciconiiformes
- Coliiformes
- Columbiformes
- Coraciiformes
- Cuculiformes
- Eurypygiformes
- Falconiformes
- Galliformes
- Gaviiformes
- Gruiformes
- Leptosomiformes
- Mesitornithiformes
- Musophagiformes
- Nyctibiiformes
- Opisthocomiformes
- Otidiformes
- Passeriformes
- Pelecaniformes
- Phaethontiformes
- Phoenicopteriformes
- Piciformes
- Podargiformes
- Podicipediformes
- Procellariiformes
- Psittaciformes
- Pterocliformes
- Rheiformes
- Sphenisciformes
- Steatornithiformes
- Strigiformes
- Struthioniformes
- Suliformes
- Tinamiformes
- Trogoniformes